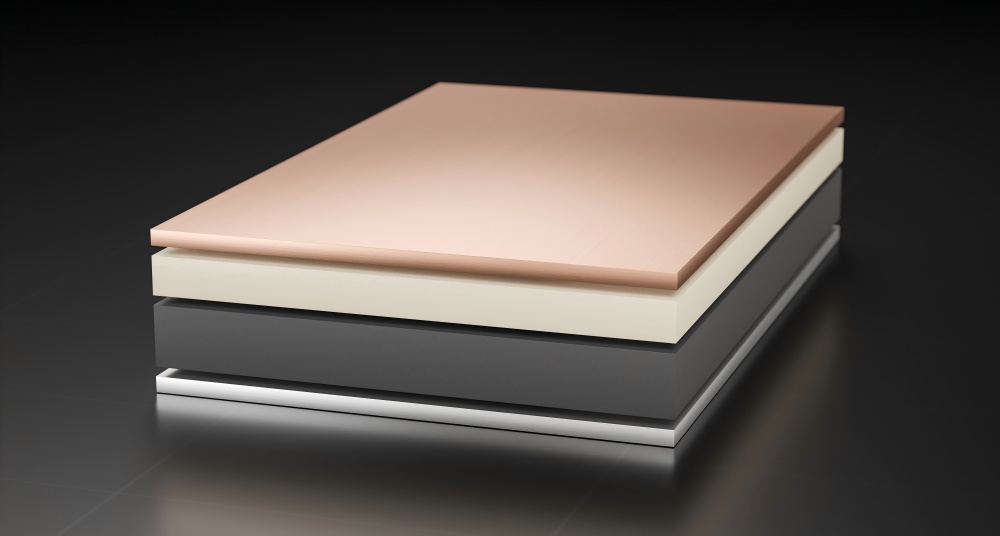
Analyze the real safety performance of solid-state batteries! Compare the thermal runaway risk of traditional lithium batteries.
Frequent fires in new energy vehicles have forced the industry to accelerate technological breakthroughs. The solid-state batteries that car companies are pushing have been "demystified" by experts recently. Although its solid electrolyte can block the risk of flammable leakage of liquid electrolytes in traditional lithium batteries from a physical level (thermal runaway temperature soars to 600°C vs. 120°C for liquid lithium batteries), "absolute safety" is still a false proposition. The core contradiction points to three hidden mines:
(1)High nickel positive electrode releases highly toxic SO₂ gas when encountering sulfide electrolyte at high temperature;
(2)Dendrites derived from lithium metal negative electrode may pierce the electrolyte and cause short circuit;
(3)Dry/wet process defects lead to local thermal runaway.
Among the current mainstream lithium battery technology routes, although the energy density of lifepo4 battery is slightly inferior in the power field, it has become the ballast stone of energy storage scenarios with its high thermal stability. Experts pointed out that the commercialization of solid-state batteries needs to cross the three levels of materials, interfaces, and manufacturing: the cost of sulfide electrolytes is 5 times that of traditional lithium batteries, and the interface modification technology of lithium negative electrodes is still in the laboratory stage. In the short term, the rechargeable battery system equipped with the lifepo4 battery will still be the mainstay of the grid-level battery energy storage solution, and the semi-solid transition solution may be the first to be installed on the vehicle.
"Safety ≠ impeccable!" Li Ming, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, emphasized that "solid-state lithium batteries will reduce the probability of accidents by 90%, but it will take ten years to completely eliminate the risk." Industry data shows that in 2023, the proportion of liquid systems in the global installed capacity of power lithium batteries will still reach 87%, and the price of semi-solid battery mass-produced vehicles will be 23% higher than that of the same liquid lithium battery models. In the next five years, lithium battery technology will present a three-track parallel pattern of liquid optimization, semi-solid transition, and all-solid breakthrough, and the battery energy storage solution market may become a new battlefield for the confrontation between the lifepo4 battery and solid-state technology. The "safety anxiety" of car companies will eventually force the lithium battery ecosystem to continue to evolve.
(1)High nickel positive electrode releases highly toxic SO₂ gas when encountering sulfide electrolyte at high temperature;
(2)Dendrites derived from lithium metal negative electrode may pierce the electrolyte and cause short circuit;
(3)Dry/wet process defects lead to local thermal runaway.
Among the current mainstream lithium battery technology routes, although the energy density of lifepo4 battery is slightly inferior in the power field, it has become the ballast stone of energy storage scenarios with its high thermal stability. Experts pointed out that the commercialization of solid-state batteries needs to cross the three levels of materials, interfaces, and manufacturing: the cost of sulfide electrolytes is 5 times that of traditional lithium batteries, and the interface modification technology of lithium negative electrodes is still in the laboratory stage. In the short term, the rechargeable battery system equipped with the lifepo4 battery will still be the mainstay of the grid-level battery energy storage solution, and the semi-solid transition solution may be the first to be installed on the vehicle.
"Safety ≠ impeccable!" Li Ming, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, emphasized that "solid-state lithium batteries will reduce the probability of accidents by 90%, but it will take ten years to completely eliminate the risk." Industry data shows that in 2023, the proportion of liquid systems in the global installed capacity of power lithium batteries will still reach 87%, and the price of semi-solid battery mass-produced vehicles will be 23% higher than that of the same liquid lithium battery models. In the next five years, lithium battery technology will present a three-track parallel pattern of liquid optimization, semi-solid transition, and all-solid breakthrough, and the battery energy storage solution market may become a new battlefield for the confrontation between the lifepo4 battery and solid-state technology. The "safety anxiety" of car companies will eventually force the lithium battery ecosystem to continue to evolve.
 +86 13332949210
+86 13332949210 info@xihobattery.com
info@xihobattery.com







 Xiho
Xiho Jun 27 2025
Jun 27 2025