The truth about battery technology from the spontaneous combustion of Xiaomi's new energy vehicles: Are lithium iron phosphate batteries really safe? 99% of people don't know about the battery black technology
Recently, the spontaneous combustion of Xiaomi's new energy vehicles has triggered heated discussions among the public about the safety of power batteries. Although the specific cause of the incident has not yet been announced, this incident has once again put the question of "whether lithium iron phosphate batteries are safe" at the forefront. As the mainstream choice in the current new energy vehicle and energy storage fields, how safe are lithium iron phosphate batteries?First of all, let us understand why lithium iron phosphate batteries are called "the bulletproof vest of the battery industry"?
1.Chemical structure of lithium iron phosphate-the origin of safety gene
The cathode material of lithium iron phosphate battery is lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄), whose olivine structure has higher thermal stability. Compared with ternary lithium batteries (such as NCM/NCA), the decomposition temperature of lithium iron phosphate battery is as high as over 500°C (ternary materials are only about 200°C), and it is less likely to have thermal runaway at high temperature or overcharge. This feature allows it to remain stable under extreme conditions, significantly reducing the risk of fire.(Data support: According to the US UL 1642 puncture test, lithium iron phosphate batteries only emit smoke but no open flame after being penetrated by a steel needle, while similar ternary batteries may burn instantly.)
In addition, lithium iron phosphate batteries have significant environmental advantages: they do not contain precious metals such as cobalt and nickel, and their non-toxic and harmless properties comply with environmental regulations such as the EU RoHS, solving safety risks in battery recycling.
In addition, lithium iron phosphate batteries have significant environmental advantages: they do not contain precious metals such as cobalt and nickel, and their non-toxic and harmless properties comply with environmental regulations such as the EU RoHS, solving safety risks in battery recycling.
2.Lithium iron phosphate production process - safety guarantee
The production process of lithium iron phosphate batteries also enhances safety. Its core processes (such as batching, coating, and winding) form a uniform voltage platform by optimizing the material particle size, further ensuring stable working conditions.
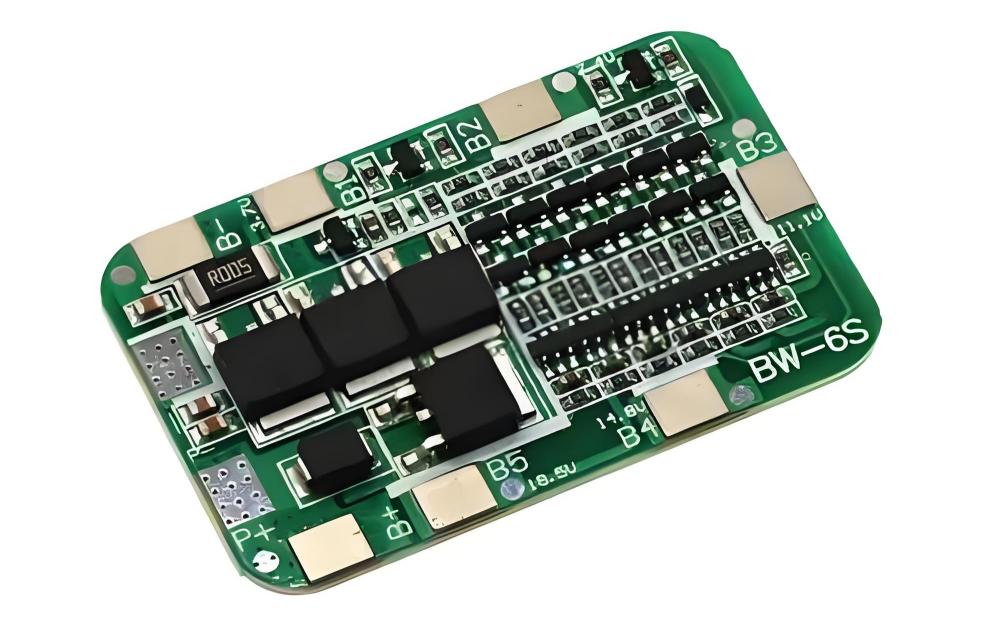
3.Lithium iron phosphate battery system safety
The lithium iron phosphate battery BMS system scans the battery health 5,000 times per second, warns of abnormalities 48 hours in advance, and automatically cuts off the circuit at a speed of 0.01 seconds. The BMS monitors multiple parameters such as voltage, current, and temperature in real time, and combines accident management data to greatly reduce the possibility of rapid spontaneous combustion of lithium iron phosphate batteries, thereby reducing the risk of ternary lithium batteries by 1/4.
At present, lithium iron phosphate batteries have been widely used in new energy vehicles, energy storage power stations and outdoor power supply fields.
For example
New energy vehicles: BYD Blade Battery (lithium iron phosphate) has passed the "needle puncture test" to verify safety and become an industry benchmark.
Energy storage system: Tesla Megapack energy storage equipment uses lithium iron phosphate batteries to meet the stability requirements under high-load scenarios.
Consumer electronics: Xiaomi, Huawei and other brands' outdoor power products are gradually turning to lithium iron phosphate batteries, focusing on "zero explosion risk".
These cases show that the safety of lithium iron phosphate batteries has been verified through large-scale applications, and safety is the "lifeline" of lithium iron phosphate batteries. However, the recent spontaneous combustion incident of Xiaomi's new energy vehicles has also sounded the alarm for the industry - even if lithium iron phosphate batteries have material-level safety advantages, they still need to build a solid safety line through technological innovation and strict management. Safety does not mean absolute safety, but lithium iron phosphate batteries are still the "safest choice."
At present, lithium iron phosphate batteries have been widely used in new energy vehicles, energy storage power stations and outdoor power supply fields.
For example
New energy vehicles: BYD Blade Battery (lithium iron phosphate) has passed the "needle puncture test" to verify safety and become an industry benchmark.
Energy storage system: Tesla Megapack energy storage equipment uses lithium iron phosphate batteries to meet the stability requirements under high-load scenarios.
Consumer electronics: Xiaomi, Huawei and other brands' outdoor power products are gradually turning to lithium iron phosphate batteries, focusing on "zero explosion risk".
These cases show that the safety of lithium iron phosphate batteries has been verified through large-scale applications, and safety is the "lifeline" of lithium iron phosphate batteries. However, the recent spontaneous combustion incident of Xiaomi's new energy vehicles has also sounded the alarm for the industry - even if lithium iron phosphate batteries have material-level safety advantages, they still need to build a solid safety line through technological innovation and strict management. Safety does not mean absolute safety, but lithium iron phosphate batteries are still the "safest choice."
 +86 13332949210
+86 13332949210 info@xihobattery.com
info@xihobattery.com







 Xiho
Xiho Apr 14 2025
Apr 14 2025